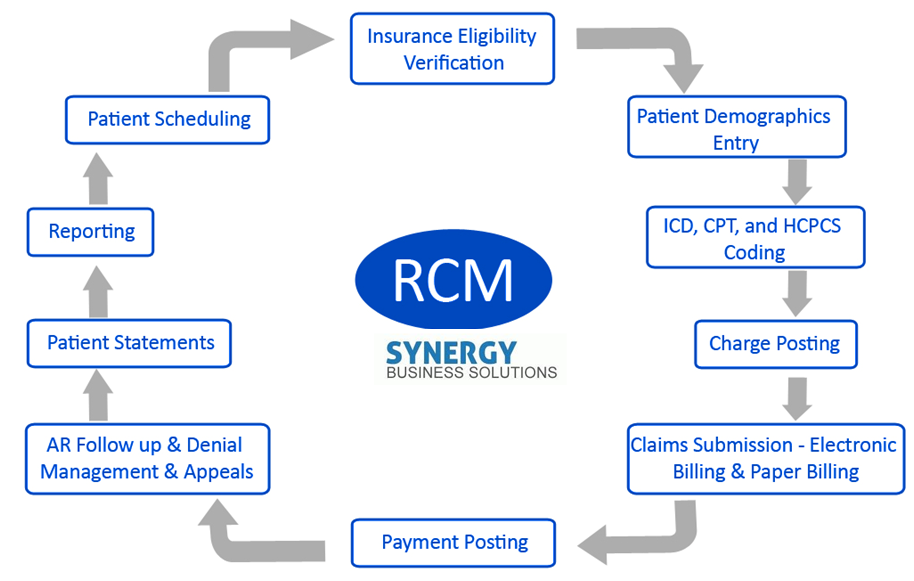
The intricate landscape of healthcare finance necessitates a profound understanding and collaboration among various departments. The revenue cycle, pivotal in optimizing income, is not solely the realm of billing or finance; rather, it is a synergy that engages multiple sectors across the healthcare continuum. Below is an exploration of the various departments that actively support and collaborate with the revenue cycle.
1. Administration
At the helm of every healthcare organization, the administration plays a vital role in the revenue cycle. Senior leadership, encompassing the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and Chief Executive Officer (CEO), is responsible for strategic oversight. Their vision influences budgeting processes, financial planning, and resource allocation, thereby establishing a framework within which the revenue cycle operates. Moreover, the administration develops policies that ensure compliance with regulations, thus providing a degree of assurance that income will be generated responsibly and ethically.
2. Clinical Departments
The connection between clinical departments—such as surgery, cardiology, and emergency services—and the revenue cycle cannot be overstated. These teams are instrumental in documenting patient care accurately. The significance of clinical documentation is immense; it directly impacts coding accuracy, which in turn affects reimbursement rates. Moreover, clinical departments are often responsible for patient consent forms and pre-authorization processes, both key elements that streamline the revenue cycle and bolster cash flow.
3. Health Information Management (HIM)
The HIM department serves as the custodian of patient data. Their responsibilities extend to ensuring the accuracy and confidentiality of health records. Effective collaboration with the revenue cycle is achieved through meticulous coding, which translates clinical services into billable revenue. HIM professionals must stay abreast of coding updates and regulations, ensuring that healthcare providers are compensated fairly for their services. Thus, HIM not only fortifies the financial viability of the organization, but also upholds the quality of care delivered.
4. Billing and Collections
This department is perhaps the most directly involved in the revenue cycle. Billing and collections personnel are tasked with generating claims and managing accounts receivable. Their efficiency influences cash flow, as they handle everything from patient invoicing to follow-up on denied claims. This department must also collaborate closely with insurers to resolve discrepancies and ensure timely payments. The interplay of billing accuracy and prompt follow-up fundamentally determines the financial health of the organization.
5. Compliance
Regulatory compliance is indispensable within any healthcare entity. The compliance department ensures that all practices adhere to federal and state regulations, including those pertaining to billing and reimbursement. Their collaboration with the revenue cycle mitigates risks of audits and penalties, safeguarding the financial interests of the organization. This continuous vigilance ensures that the revenue cycle functions within a legal and ethical framework, thereby fostering a sustainable financial model.
6. Information Technology (IT)
In an increasingly digitized healthcare landscape, the role of IT is paramount. This department supports the revenue cycle through the implementation and maintenance of electronic health records (EHR) systems and billing software. IT professionals are essential in ensuring that these systems are integrated and functioning optimally, thus facilitating seamless data flow between patient care and billing operations. Moreover, they play a crucial role in data security, protecting sensitive financial information against unauthorized access.
7. Marketing and Patient Services
The marketing department fosters patient engagement, which is essential for revenue generation. They develop strategies to attract new patients and retain existing ones, utilizing data analytics to target demographics effectively. Collaborating with patient services is vital, as it directly influences patient satisfaction and loyalty. When patients are educated about their financial responsibilities and insurance coverage, it streamlines the revenue process and can lead to a more stable cash flow.
8. Human Resources
Human resources (HR) significantly impact the revenue cycle through workforce management. By recruiting and retaining qualified personnel, HR addresses the need for skilled professionals in billing, coding, and compliance. Training and development programs also play a crucial role in maintaining staff expertise. The quality of human capital directly correlates with operational efficiency, ultimately affecting the organization’s bottom line.
9. Finance and Accounting
Last but not least, the finance and accounting department provides critical support to the revenue cycle. Beyond merely tracking income and expenses, they conduct financial analysis to identify trends and anomalies. This empirical data informs strategic decision-making. Furthermore, finance professionals are responsible for financial reporting and forecasting, allowing the organization to anticipate cash flow needs and adjust strategies accordingly.
In conclusion, the revenue cycle thrives on collaboration among an array of departments, each contributing unique expertise and essential functions. An effective revenue cycle management system is not merely about billing but encompasses a comprehensive approach that integrates clinical accuracy, regulatory compliance, technological infrastructure, and patient engagement. When all these components work in concert, organizations can enhance financial stability, ensuring the sustainability of quality healthcare services.
