In the vast and intricate world of network management, one often encounters a myriad of fascinating components that work in harmony to ensure seamless communication between devices. Among these, the Domain Name System (DNS) serves as an essential pillar. But, have you ever pondered: Which DHCP option is utilized to specify the DNS suffix? This question not only tailors to the curiosity of network administrators but also poses a challenge, as the answer lies within the multifaceted realms of Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) options.
To facilitate a comprehensive understanding, it is imperative first to explore the fundamental concepts of DHCP. DHCP is a network management protocol used on IP networks where a DHCP server dynamically assigns IP addresses and other configuration parameters to each device on the network. This alleviates the manual configuration burden for network administrators and ensures efficient usage of the IP address space.
Within the domain of DHCP, options are defined parameters that extend the functionality of the protocol, allowing for greater customization based on specific network requirements. Each option has a unique code and serves a specific purpose. Among the plethora of options available, the one that holds particular relevance to DNS configuration is Option 15, typically referred to as the “Domain Name Option.”
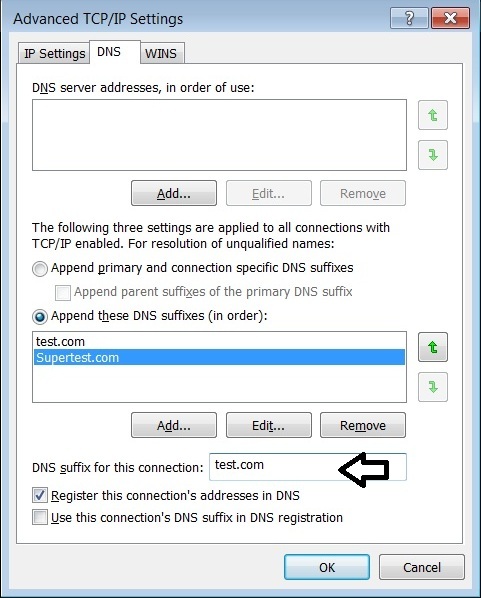
Option 15 is crucial as it allows the DHCP server to communicate the DNS suffix to the client devices. This suffix is appended to unqualified hostname requests, ensuring that any outgoing domain queries are properly resolved within the specified domain. But why does this matter? Imagine a scenario where users on a corporate network need to access internal resources. Without a correctly configured DNS suffix, users may find themselves grappling with connection failures, as their machines would not recognize the appropriate domain for resolution.
To elucidate the significance of this option further, consider its application in various networking environments. For instance, in large enterprises, where numerous subdomains and services exist, a well-defined DNS suffix becomes a cornerstone for effective resource access. It streamlines the user experience, promotes efficiency, and enhances overall network performance.
However, the implementation of Option 15 is not without its potential pitfalls. Misconfiguration can lead to a plethora of issues, including DNS resolution failures, connectivity problems, and increased administrative overhead. Therefore, understanding the broader implications of using this particular DHCP option is paramount for ensuring robust network functionality.
So, how does one configure Option 15 in a DHCP environment? The process can vary based on the operating system and DHCP server software being utilized. For instance, in a Windows Server environment, a DHCP administrator might navigate to the DHCP management console, select the appropriate scope, and then add Option 15 under the “Server Options” or “Scope Options.” This would entail entering the desired DNS suffix, thereby enabling all clients within that scope to receive this configuration during the DHCP lease process.
In contrast, on a Linux-based DHCP server, the DHCP configuration file, often located at /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf, would need to be modified. The syntax for implementing Option 15 might resemble the following:
option domain-name "example.com";This simplistic line signifies to client devices that any unqualified hostname should be suffixed with “example.com,” ensuring proper resolution within that domain.
In addition to its basic functionality, the DNS suffix options can be pivotal during transitions, such as mergers or acquisitions, where unifying disparate domain environments is essential. Properly configuring Option 15 facilitates smoother integration, minimizes disruption, and helps maintain operational continuity.
Moreover, as technology continues to burgeon, overlaying complexity onto previously simple network paradigms, the traditional role of DHCP and DNS must evolve to meet new demands. Configuring DNS suffixes is increasingly relevant in contemporary networking scenarios, such as cloud deployments, multi-tenant architectures, and mobile environments where seamless connectivity is paramount.
However, network administrators must remain vigilant regarding the implications of DNS suffixes on security. For instance, incorrect suffix configurations can expose networks to DNS poisoning attacks, where malicious actors might redirect legitimate traffic to harmful sites. This underscores the necessity of a thorough understanding of the DHCP Option 15 configuration and its associated risks.
In conclusion, although the question regarding which DHCP option is utilized to specify the DNS suffix might seem straightforward, its implications and best practices are anything but simplistic. Option 15 serves as a critical element within the DHCP framework, profoundly impacting client device behavior and overall network performance. Network administrators must ensure proper configuration to harness the full potential of this option, promoting efficient and secure access to resources across their networks.
Thus, as technology progresses and networks evolve, mastering the intricacies of DHCP options, particularly Option 15, will remain an indispensable endeavor for any proficient network manager. Whether one operates in small businesses or vast enterprises, understanding and effectively deploying this option is crucial to navigating the complexities of modern networking.
